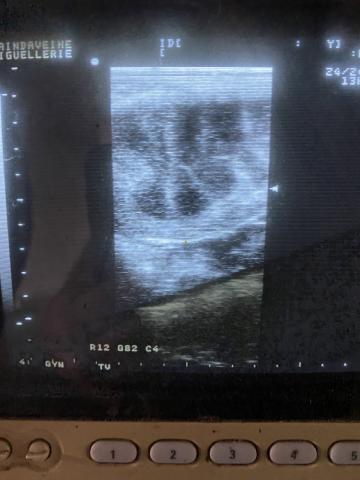
The gynecological follow-up of your mare consists of a series of regular examinations, carried out by the veterinarian, to monitor her reproductive health and to make sure that she is in good condition for reproduction, and that she is inseminated under ideal conditions.
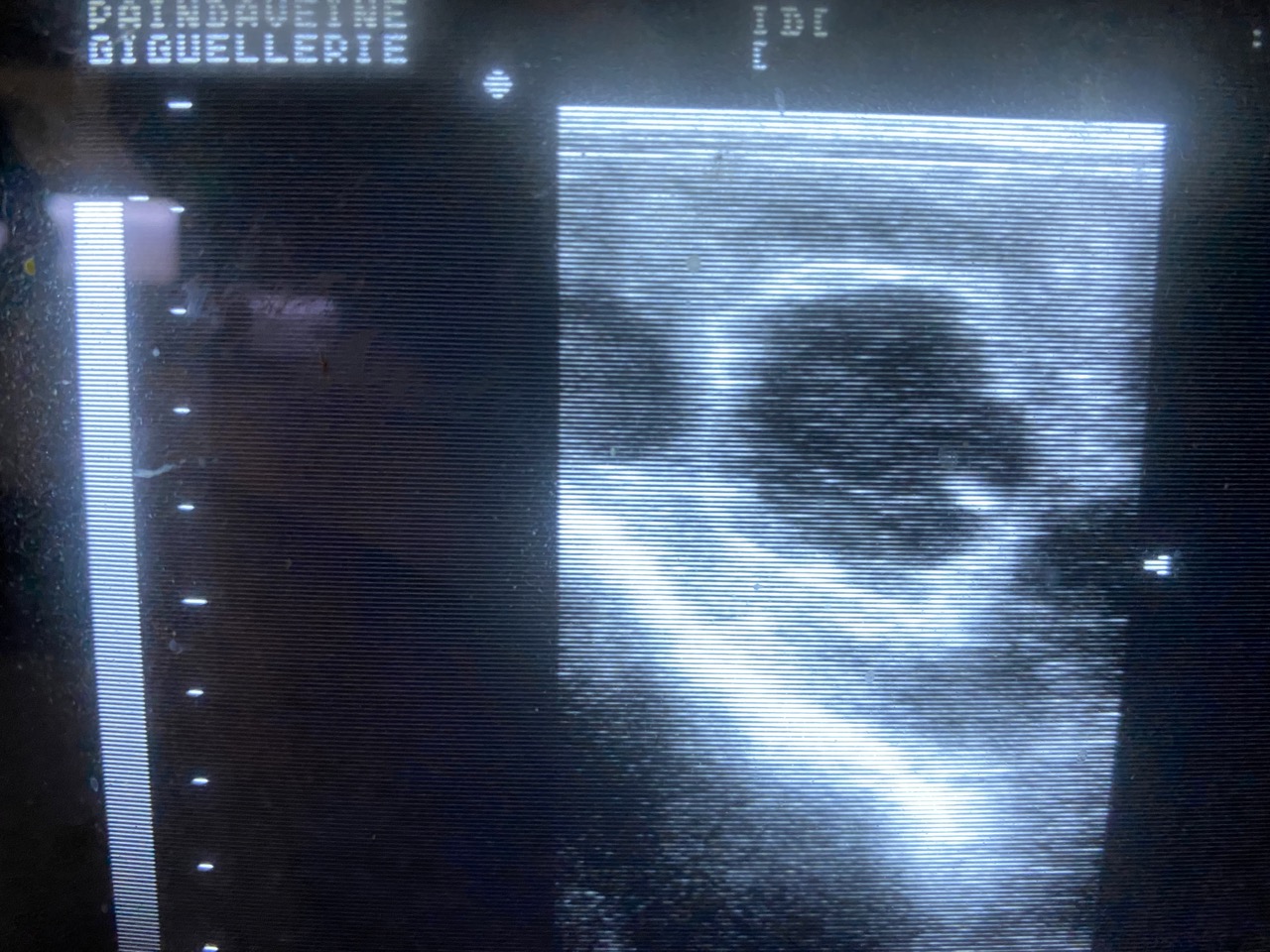 This may include physical and ultrasonographic examinations, blood tests, cytological sampling, and many other procedures. The goal is to detect and treat any reproductive health problems in a timely manner, and to inseminate your mare in a window of time conducive to fertilization, to maximize the chances of successful reproduction.
This may include physical and ultrasonographic examinations, blood tests, cytological sampling, and many other procedures. The goal is to detect and treat any reproductive health problems in a timely manner, and to inseminate your mare in a window of time conducive to fertilization, to maximize the chances of successful reproduction.
In general, gynecological monitoring of a mare that is inseminated with frozen semen is more intense than that of a mare that is traditionally inseminated, as it is important to ensure that the frozen semen is deposited in the uterus within a short window of time near ovulation.
The veterinarian pays attention to several organs during the gynecological monitoring of the mare, including:
- Ovaries: to detect signs of ovulation and ensure that the ovaries are functioning properly.
- Uterus: to check for infections and physiological disorders to avoid abortions, fetal death, etc.
- Fallopian tubes: to make sure that they are in good condition and can properly transmit the fertilized egg to the uterus.
- Vagina: to check for lesions or infections that may affect the mare's ability to conceive.
- Vulva: to observe any conformation abnormalities that may also affect the reproductive health of the mare, but also lead to problems during foaling, such as difficult births, vulvar tears or complications for the fetus.
The veterinarian performs a series of physical examinations, ultrasounds, and sometimes laboratory tests to monitor the condition of these organs and to ensure that the mare is in good reproductive health.
Finally, special attention is paid to semen quality, which is extremely important to the success of an insemination.
Adequate semen quality is necessary to ensure that the sperm are viable and in sufficient numbers to fertilize the egg.
Sperm of inferior quality may be defective or in insufficient numbers, which can result in a low conception rate and a reduction in the number of live births. Sperm must also be healthy to be able to function properly and penetrate the egg to fertilize it.
 We can assess semen quality by performing laboratory tests to measure sperm quantity, motility and morphology. If there are problems with semen quality, there may be various options for improving quality, such as medical treatment, nutritional management or modification of the reproductive program.
We can assess semen quality by performing laboratory tests to measure sperm quantity, motility and morphology. If there are problems with semen quality, there may be various options for improving quality, such as medical treatment, nutritional management or modification of the reproductive program.
In summary, semen quality is critical to the success of an insemination because it influences the ability of the sperm to fertilize the egg and produce a live foal. Therefore, it is important to monitor semen quality to maximize the chances of successful breeding.
Add new comment